Cannabinoids: Understanding its Effects and Benefits
Cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, are chemical compounds found in Cannabis Sativa with various effects on the mind and body. THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, while CBD is believed to have anti-psychotic properties. These compounds can influence mood, memory, sleep, and appetite. Synthetic cannabinoids, like HU-210 and JWH, mimic the effects of THC but carry additional risks. Medical applications include treating epilepsy, pain, and inflammation. Cannabinoids interact with specific receptors in the brain, which impacts brain function and neurotransmission. Regulations and safety considerations play a crucial role in cannabinoid usage.
Table of Contents
Effects of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids have various effects on the mind and body, influencing different aspects of human functioning. These effects are primarily attributed to the two main cannabinoids found in Cannabis Sativa: delta-9-tetrahidrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
Psychoactive Effects of THC
THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with cannabis use. When consumed, THC interacts with receptors in the brain, leading to alterations in perception, cognition, and mood. Users may experience feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and increased sociability. However, THC can also induce anxiety, paranoia, and impaired coordination.
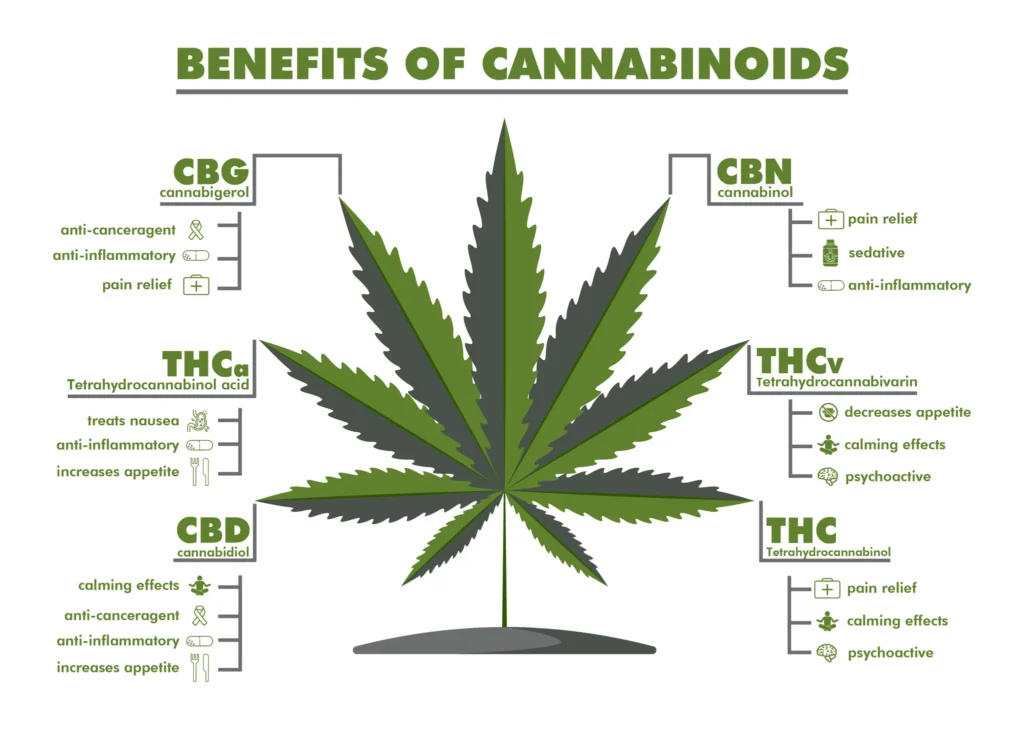
Anti-psychotic Properties of CBD
CBD, on the other hand, is believed to have anti-psychotic properties and counteract some of the negative effects of THC. It does not produce psychoactive effects and may even mitigate the anxiety and paranoia associated with THC consumption. CBD is also being explored for its potential therapeutic benefits in various medical conditions.
Impact on Mood and Mental State
Cannabinoids can significantly influence mood and mental state. While THC may induce feelings of relaxation and euphoria, it can also lead to anxiety and temporary memory impairment. CBD, on the contrary, is considered non-intoxicating and may have calming effects, potentially alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Influence on Memory and Cognitive Function
THC can affect memory and cognitive function, impairing short-term recall and attention. Long-term use of THC-rich cannabis may have negative implications for cognitive abilities, especially in heavy and persistent users. CBD, however, may have a neuroprotective effect and could potentially mitigate cognitive decline.
Effects on Sleep and Appetite
Cannabinoids have demonstrated effects on sleep patterns and appetite regulation. THC, for instance, may induce drowsiness and promote sleep, but chronic use can disrupt sleep architecture. Additionally, THC is known to stimulate appetite, often leading to increased food intake, commonly referred to as “the munchies.” CBD’s impact on sleep and appetite requires further investigation.
In summary, cannabinoids like THC and CBD have a range of effects on the mind and body. While THC produces psychoactive effects and can alter mood, cognition, and memory, CBD is believed to have anti-psychotic properties and may counteract some negative effects of THC. The influence on mood, mental state, memory, cognitive function, sleep, and appetite has important implications for cannabis users and underscores the need for further research in these areas.
Synthetic Cannabinoids and Drug Abuse
Synthetic cannabinoids refer to lab-created substances designed to mimic the effects of natural cannabinoids like THC. They are often marketed as legal alternatives to cannabis. However, understanding these synthetic compounds is crucial due to their associated risks and dangers.
Understanding Synthetic Cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids are chemically engineered substances that interact with the same receptors as natural cannabinoids. They are typically sprayed onto plant material and marketed as herbal incense or potpourri. These products are easily accessible, sold online, and in various retail outlets, making them attractive to individuals seeking recreational drug alternatives.
Risks and Dangers of Synthetic Cannabinoids
The use of synthetic cannabinoids carries significant risks and dangers. Unlike natural cannabinoids, these lab-created substances often have unknown chemical compositions, making dosage unpredictable and potentially hazardous. Synthetic cannabinoids can lead to severe and even life-threatening side effects, including anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations, rapid heart rate, and seizures. In some cases, the use of synthetic cannabinoids has resulted in hospitalizations and fatalities.
The lack of regulation and oversight in the production of synthetic cannabinoids poses additional dangers. Manufacturers frequently alter the chemical composition of these substances to evade legal restrictions, resulting in an ever-evolving array of potentially harmful compounds. The constant variations make it difficult for authorities to enforce effective control and restriction measures.
Synthetic Cannabinoids vs. Natural Cannabinoids
It is important to distinguish synthetic cannabinoids from their natural counterparts. While natural cannabinoids found in cannabis plants undergo cultivation and extraction processes, synthetic cannabinoids are entirely human-made in laboratory settings. The manufacturing process allows for greater consistency and control over the chemical composition and potency of synthetic cannabinoids.
However, the key concern lies in the fundamental differences in effects and safety. Natural cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, have been subject to more research and have well-established safety profiles when used responsibly and in controlled settings. Synthetic cannabinoids, in contrast, have less understood properties due to the ever-changing chemical formulations, leading to potentially unpredictable and dangerous consequences.
- Synthetic cannabinoids pose distinct risks:
- Greater potential for adverse reactions and toxicity
- Unknown long-term effects on physical and mental health
- Increase the likelihood of addiction and dependence
- Increased potential for dangerous drug interactions
Overall, synthetic cannabinoids present significant dangers and should be approached with extreme caution. Engaging in drug abuse involving these substances can have severe consequences for individuals’ health and well-being.
Medical Uses and Health Benefits
The potential medical applications of cannabinoids have garnered significant interest in recent years. Research suggests that cannabis-based medications may offer therapeutic benefits in various health conditions. Here, we explore the medicinal potential of cannabinoids, with a focus on cannabidiol (CBD) and its role in treating epileptic syndromes, pain management, inflammation, and potential applications in neurological disorders.
Medicinal Cannabis and its Therapeutic Potential
Medicinal cannabis refers to the use of cannabis or its derivatives for medicinal purposes. The plant’s cannabinoids have shown potential in alleviating symptoms associated with various health conditions. Ongoing research aims to uncover the therapeutic potential of cannabinoid-based treatments further.
CBD as a Treatment for Epileptic Syndromes
One area where CBD has shown promise is in the treatment of epileptic syndromes, particularly in children. Clinical studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures in certain forms of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Cannabinoids in Pain Management and Inflammation
Cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, have been investigated for their potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds may offer alternative options for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions, such as neuropathic pain, arthritis, and cancer-related pain.
Moreover, cannabinoids have shown promise in reducing inflammation associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Their ability to modulate the immune response and alleviate inflammation provides avenues for further exploration in the field of pain management and inflammation.
Exploring Potential Applications in Neurological Disorders
Emerging research suggests that cannabinoids may hold therapeutic potential in various neurological disorders. For example, CBD has shown neuroprotective effects and may help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
The interaction of cannabinoids with the endocannabinoid system in the brain offers promising avenues for the development of novel treatments in neurology. However, further studies and clinical trials are necessary to fully understand the mechanisms and evaluate the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating neurological disorders.
While cannabinoids show promise in various medical applications, it is crucial to conduct further research and establish effective dosing guidelines. Additionally, the safety and potential side effects of cannabinoid-based treatments should be carefully evaluated to ensure optimal patient care and regulatory compliance.
Overall, the ongoing exploration of cannabinoids’ medical uses and health benefits presents new possibilities for treating a range of conditions. Continued research efforts aim to uncover the full potential of cannabinoids in improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with various medical conditions.
Cannabinoid Receptors and Brain Function
Understanding the role of cannabinoid receptors in the brain is crucial to comprehending the effects of cannabinoids on our central nervous system. These receptors, known as CB1 and CB2 receptors, play a significant role in regulating various brain functions and neurotransmission.
CB1 and CB2 Receptors: An Overview
CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are predominantly present in immune cells and peripheral tissues. CB1 receptors are responsible for mediating the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids, impacting mood, memory, and motor coordination. On the other hand, CB2 receptors play a role in the immune response and inflammation regulation.
These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and naturally occurring cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) that are produced by our bodies. The binding of cannabinoids, whether naturally produced or derived from cannabis, to these receptors influences various physiological processes.
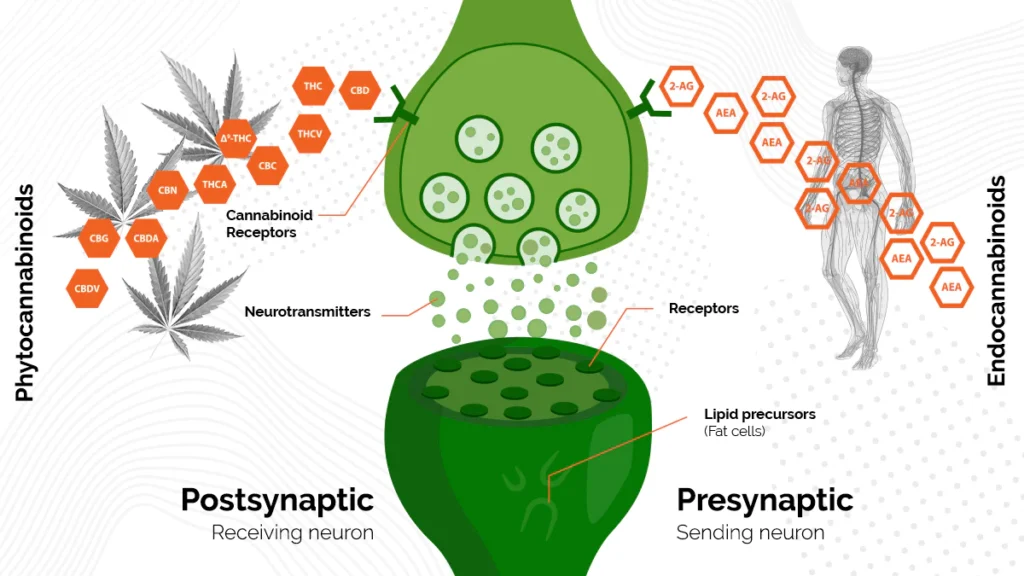
How Cannabinoids Interact with the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system by binding to and activating CB1 and CB2 receptors. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they can modulate the release of neurotransmitters, affecting neuronal activity and communication within the brain.
CB1 receptors, when activated by cannabinoids, can have both inhibitory and excitatory effects on neurotransmitter release. This modulation can impact mood, memory, reward, and pain perception. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, regulate immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival.
Implications for Brain Function and Neurotransmission
The activation of cannabinoid receptors and the subsequent modulation of neurotransmitter release can have profound implications for brain function. Cannabinoids, such as THC, interact with CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to psychoactive effects and alterations in cognitive processes.
Moreover, the endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the brain and regulating various physiological processes. Dysregulation of the endocannabinoid system has been implicated in several neurological disorders, including epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Understanding the intricate relationship between cannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and brain function is vital for unraveling the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in various neurological conditions. Ongoing research aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which cannabinoids affect neurotransmission and develop targeted therapies to harness their therapeutic benefits.
Safety and Regulations Concerning Cannabinoids
Government and Medical Community Perspectives
The safety and regulation surrounding cannabinoids have been a subject of great concern among government bodies and the medical community. While there is an increasing acceptance of the medical benefits of cannabinoids, there are still varying perspectives on their overall safety and recreational use. Government bodies, such as the FDA, are closely monitoring the impact of cannabinoids on public health and evaluating their potential risks and benefits. The medical community plays a crucial role in providing insights based on scientific research, clinical trials, and patient outcomes.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
It is important to understand the potential side effects and risks associated with cannabinoid use. While some individuals may experience beneficial effects, others may be more susceptible to adverse reactions. Common side effects may include dizziness, dry mouth, impaired coordination, and short-term memory impairment. Additionally, long-term or heavy use of cannabinoids has been associated with potential cognitive impairments and increased risk of mental health disorders, especially in vulnerable populations such as adolescents.
Specific Risks in Certain Populations
- Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals: The use of cannabinoids during pregnancy and while breastfeeding can have potential risks to the developing fetus and newborn. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential.
- Individuals with cardiovascular conditions: Cannabinoids have been known to increase heart rate and blood pressure, potentially posing risks for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Individuals with mental health disorders: While cannabinoids hold promise for certain mental health conditions, they may also exacerbate symptoms or increase the risk of psychosis in susceptible individuals.
Interactions with Other Medications
- It is important to be aware of potential interactions between cannabinoids and other medications. Cannabinoids can affect the metabolism of certain drugs, leading to altered blood concentrations and potential adverse reactions.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial for individuals taking medications that may interact with cannabinoids, including but not limited to anti-epileptic drugs, blood thinners, and antidepressants.
Legal Considerations and Usage Guidelines
The legal status of cannabinoids can vary depending on state laws and regulations. While some states in the US have legalized the medical or recreational use of cannabinoids, others maintain stricter regulations. It is essential to understand and comply with the specific laws of the state in which one resides or intends to use cannabinoids. Additionally, adherence to usage guidelines, such as appropriate dosing and responsible consumption, is fundamental for minimizing potential risks and ensuring the safe use of cannabinoids.
As the understanding of cannabinoids continues to evolve, it remains imperative to stay informed about the latest research findings, medical recommendations, and legal developments. Being aware of the potential risks, governmental perspectives, and guidelines for using cannabinoids provides a foundation for making informed decisions regarding their usage.

Post Comment